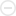
This is probably a repost, but I doubt you've seen the pictures along with relevant information on the motor. I got tired of seeing this in pieces and decided to put it all together. If I'm missing anything please let me know.
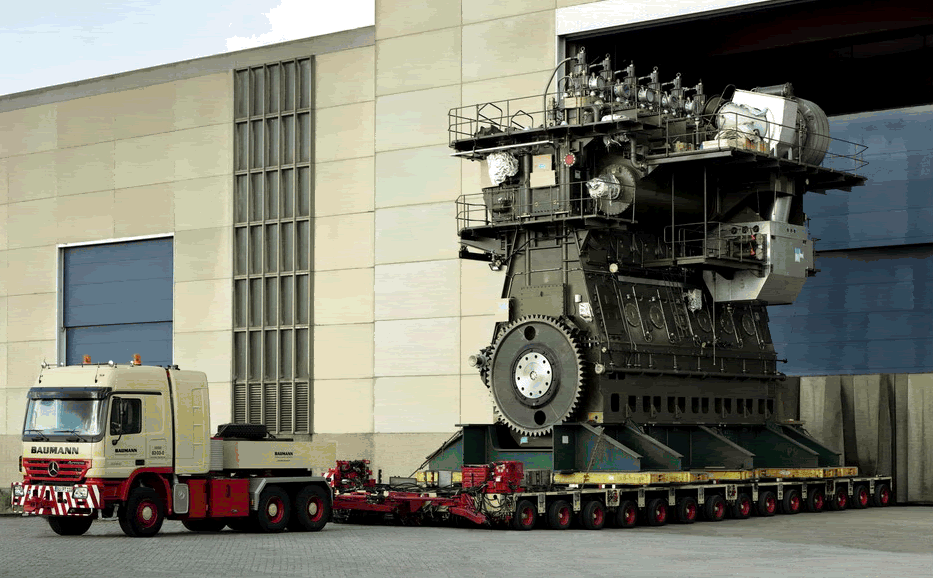
The Wartsila-Sulzer RTA96-C turbocharged valved two-stroke HFO engine (similar to diesel train engines) is the most powerful and most efficient prime-mover in the world today. Though Wartsila is a Finnish company, Aioi Works of Japan 's Diesel United, Ltd built the first engines and is where some of these pictures were taken. It is available in 6 through 14 cylinder versions, all are inline engines. These engines were designed primarily for very large container ships. Ship owners like a single engine/single propeller design and the new generation of larger container ships needed a bigger engine to propel them.
The cylinder bore is just under 38" and the stroke is just over 98". Each cylinder displaces 111,143 cubic inches (1820 liters) and produces 7780 horsepower. Total displacement comes out to 1,556,002 cubic inches (25,480 liters) for the fourteen cylinder version.
Some facts on the 14 cylinder version:
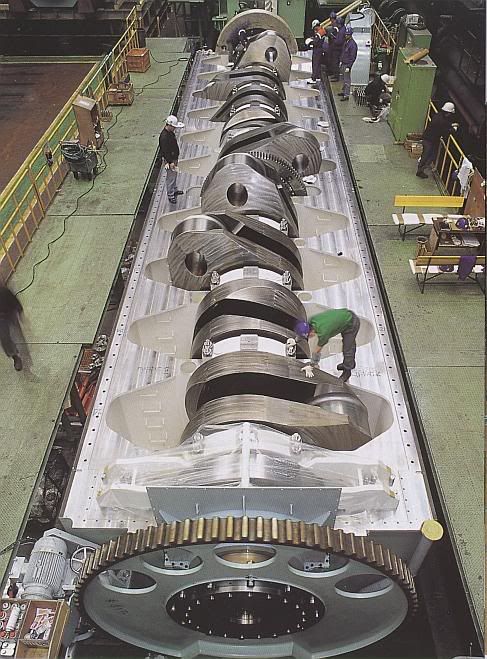
Total engine weight: 2300 tons (The crankshaft alone weighs 300 tons.)
Length: 89 feet
Height:44 feet
Maximum power: 108,920 hp at 102 rpm NO VTEC. Only makes 4.27 HP/l - What a POS
Maximum torque: 5,608,312 lb/ft at 102rpm
Fuel consumption at maximum power is 0.278 lbs per hp per hour (Brake Specific Fuel Consumption) . Fuel consumption at maximum economy is 0.260 lbs/hp/hour. At maximum economy the engine exceeds 50% thermal efficiency. That is, more than 50% of the energy in the fuel in converted to motion.
Most automotive and small aircraft engines have BSFC figures in the 0.40-0.60 lbs/hp/hr range and 25-30% thermal efficiency range. Even at its most efficient power setting, the big 14 consumes 1,660 gallons of heavy fuel oil per hour.
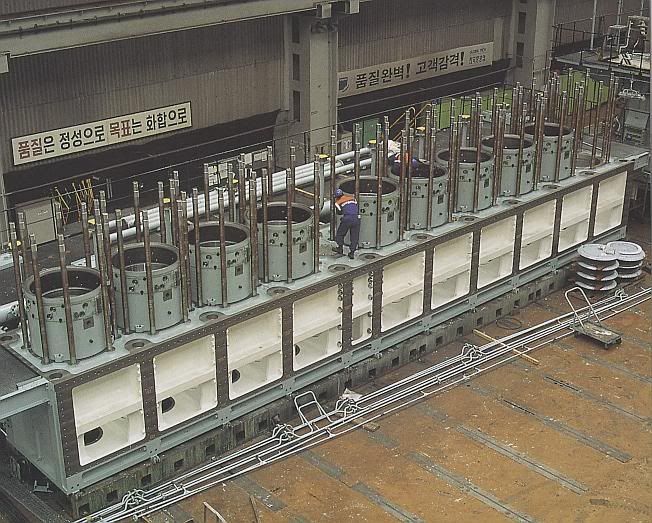
Installing the fluid bearings:
Crank:
Rods with cross journals:
Rods with pass-through piston oil squirters:
Bottom of the piston:
Assembled:
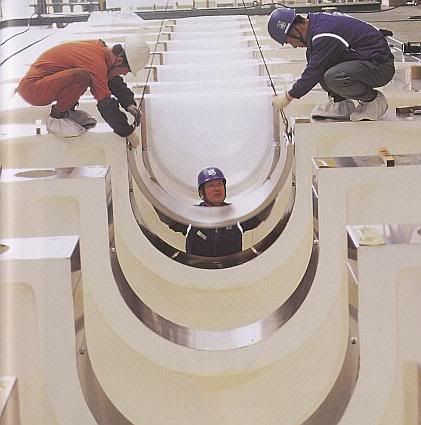
Assembly of the pistons:
A tiny 6 cylinder version:
Engine Technology:
You will notice that the camshaft has been completely eliminated and replaced with high pressure commonrail injection.
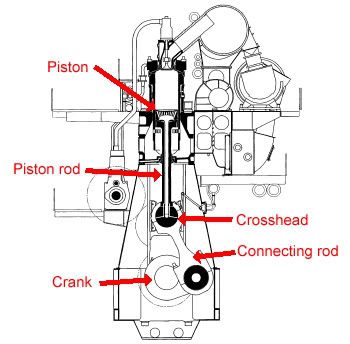
The top of the connecting rod is not attached directly to the piston. It attaches to a "crosshead" which rides in guide channels. A long piston rod then connects the crosshead to the piston.
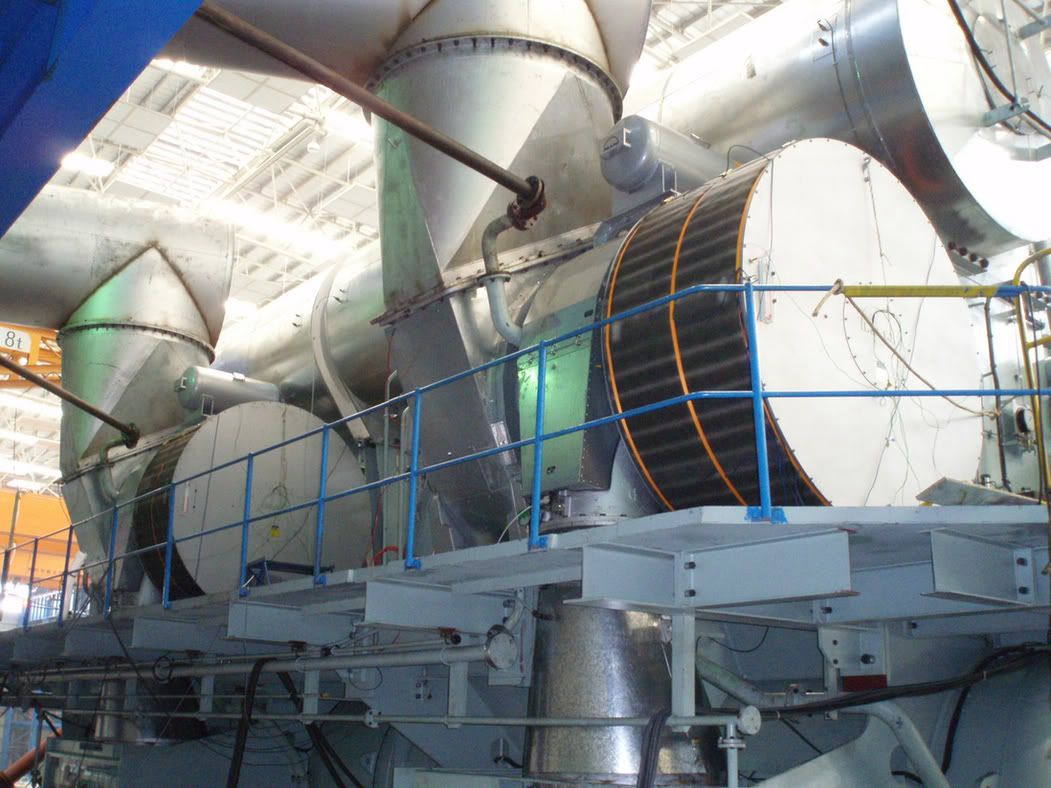
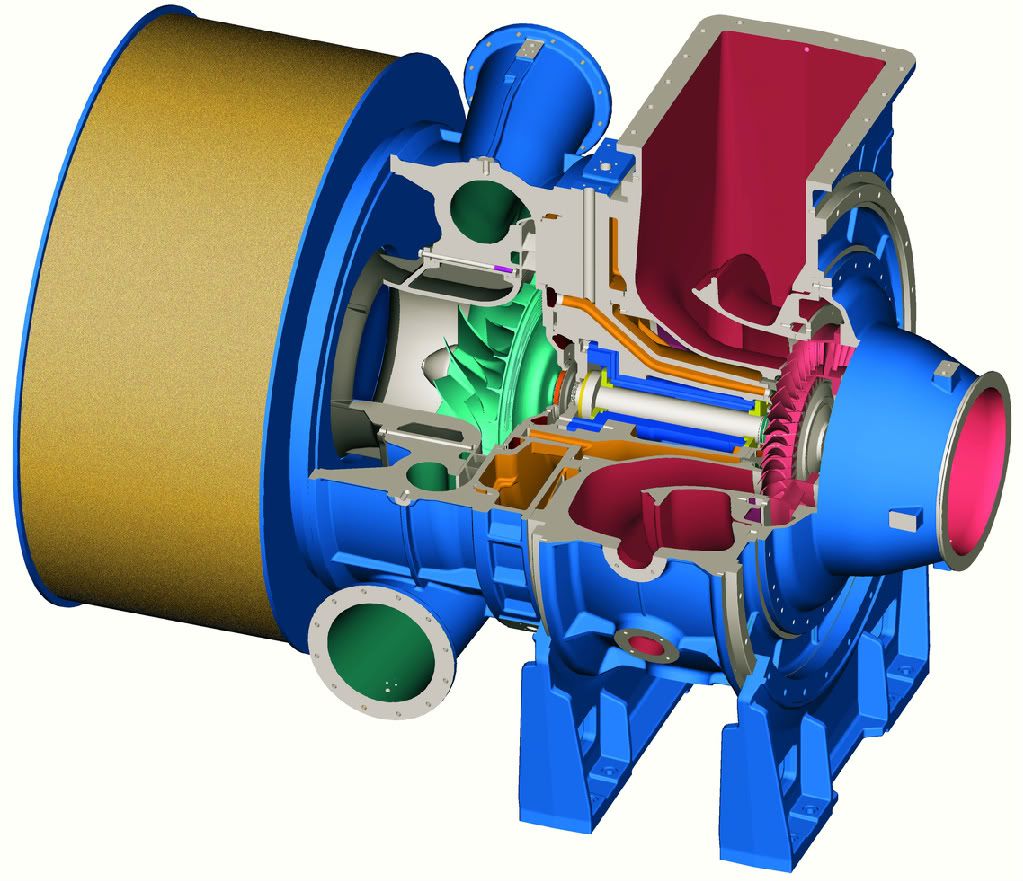
Turbocharger Technology:
Often, turbos on engines this big also have electrical generators on them or direct, mechanical drive back to the driveshaft. This is know as turbo compounding and was used originally on some bomber's radial engines, such as the famous WASP. Later versions of the V1710 Allison also had it. Most recently, Volvo, Scania (SAAB), and Detroit Diesel have used it in there truck engines. A little history lesson for the day.
[text stolen from "The Former PFR" @ Viperalley]
TWIN TURBO:
I think that's all the pics I've found on this engine series. I hope it was worth a look.













 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote


 [/URL]
[/URL]

 could this be a replacment for the "K"
could this be a replacment for the "K"